Chapter 13 the Costs of Production Questions for Review Answers
Engineering Economics and Financial Accounting - Product Function and Toll Assay - Important Questions and Answers: Production Function and Cost Analysis
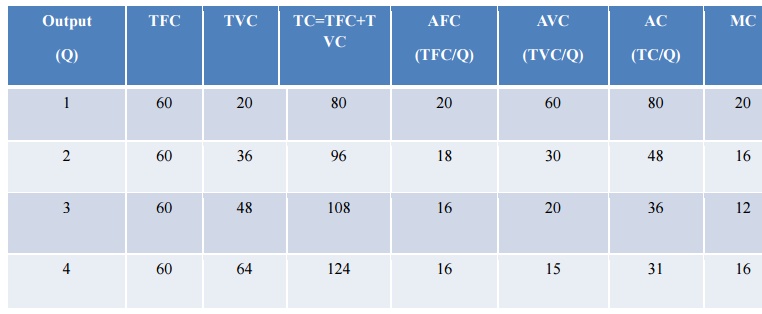
1. Say some of the main cost concepts. i) Actual costs and opportunity costs two) Incremental costs and sunk costs three) Explicit costs and implicit costs 4) By costs and time to come costs v) Accounting costs and economic costs half dozen) Direct price and indirect cost 7) Private costs and social costs viii) Controllable costs and not controllable costs ix) Replacement costs and original costs x) Shutdown costs and abandonment costs 11) Urgent costs and postponable costs 12) Bussiness costs and full sosts xiii) Fixed costs and variable costs fourteen) Short run and long run costs 15) Incremental costs and marginal costs 2. What are actual costs and opportunity costs ? Bodily costs which a firm incurs for producing or acquiring a product or a service. Equally example for this is the cost on raw materials, labor, hire, interest. 3. What are incremental costs and sunk costs ? Incremental cost is the additional cost due to change in the level of nature or concern activity. Sunk costs are the costs that are not altered by a modify in quantity produced and cannot be recovered. four. What are Explicit costs and implicit costs ? Explicit or paid out costs are those expenses which are actually paid past the business firm. Implicit costs are the theoretical costs in the sense that they go unrecognized by the bookkeeping system. 5. What are past costs and future costs ? Past costs are the bodily costs incurred in the past are generally contained in the financial accounts. Time to come costs are costs that are expected to occur in some futurity period or periods. 6. What are accounting costs and economic costs ? Bookkeeping costs are the actual outlay costs. Economic cost relate to the future, seven. What is direct and indirect toll ? Direct price are traceable price or assignable cost are the ones that have directly relationship with a unit of performance similar a production, a procedure or a product, or a department of the firm. On the otherhand, indirect costs or non traceable costs or mutual or non assignable costs are the costs whose course cannot be easily and definitely traced to the found. 8. What are private costs and social costs ? Private costs are those which are actually incurred or provided for the business activeness by an individual or the house. Social costs on the otherhand are the total costs to the club on business relationship of production of a proficient. ix. What are controllable and non controllable costs ? Controllable costs are those which are capable of being controlled or regulated by the managers pismire = d information technology can be used to appraise the managerial efficiency in controlling the cost in his section. Not controllable costs are those which cannot be subjected to administrative controls and supervision. 10. What are replacement costs and original costs ? Original costs or the historical costs are the costs paid for assets such equally land, edifice, cost of constitute, equipment and materials. Replacement costs are the costs that the firm incurs if it wants to supercede or larn the same assets at present. xi. What is shut down cost and abandonment cost ? Shutdown costs are costs in which the business firm incurs if it temporarily stop its operation. Abandonment costs are the costs of retiring altogether a fixed nugget from employ. 16)what are incremental cost and marginal cost? Incremental cost is of import when dealing with decisions where discrete alternatives are to be compared.marginal cost deals with unity unit output. 17)what are the determinants of cost? 1) level of output 2) price of inputs. 3) size of plant 4) output stability v) product lot size 6)level of adequacy utilization vii) technology 8) learning consequence 9) breadth of product range. x) geographical location 18) what are the two aspects in price output relationships? 1) cost output human relationship in short run. two)toll output relationship in long run. 19) what are the terms involved in cost output relationship? 1) Average stock-still cost. 2) Boilerplate variable cost. 3) Average total toll. twenty) what is level of chapters utilization? The higher the capacity utilization fixed cost per unit of output in bound to be low. 21) what is output stability? Stability of output leads to savings in various kinds of hidden toll interruption and learning. 22)what is size of plants? Production costs are normally lower in bigger plants than smaller plants. 23)what is cost? Cost is the money spent on producing and selling a product to the customers.the cost of a product starts from the raw materials through production costs till selling costs include the cost in maintaining outlets. 24)what is the significance of price in managerial decision making? Study of costs is essential for making a choice from among the competing production plans.production decisions are not possible without their respective toll considerations. 25)what is price of input? If the toll of the raw materials labor,power increases then naturally the cost of production goes up.this cost of productions varies directly with the prices of inputs. PART B one. Briefly explicate almost types of product office with illustration production function with i variable input Ø Increasing return Ø Negative return Ø Decrasing render production function with 2 variable input Ø iso quants Ø ii factors of product vs capital & labour Ø It gradient downwards from left to correct Ø It can't exist horizontal or vertical Ø Iso quants all convex to the origin Ø Never touch 10 axis Ø Never touch y centrality product role with all variable input Ø increasing render to calibration Ø Decreasing return to scale Ø constant return to calibration • Product function with 2 variable input Iso quant bend: It represent the dissimilar combination of inputs producing a detail quantity of output. Assumption Ø Two factor of production vs upper-case letter & labour Ø Two factor can substitute each other up to a certain limit Ø Shape of ISO quant depends upon the extent of substitutability of 2 inputs Ø Technology is given over a period of time Isoquant map An isoquant map is a ready of isoquants that shows the maximum accessible output from whatsoever given combination inputs. Types of iso quants Linear Isoquant: This type assumes perfect substitutability of factors of production: a given article may be produced past using only capital, or only labour, or by an infinite combination of K and Fifty. Input-Output Isoquant: This assumes strict complement [that is, nix substitutability] of the factors of production. The isoquant take the shape of a right angle. This type of isoquant is also called 'Leontief isoquant' later on Leontief, who invented the input-output assay. Smooth , Convex Isoquant: This form assumes continuous substitutability of Thou and L only over a certain range, beyond which factors cannot substitute each other. The isoquant appears as a smooth curve convex to the origin. Long run production part with all variable (Laws of return to scale) Return to scale refers to the relationship between changes in output and proportionate changes in all factors of production Assumptions · All factors are variable · Workers work with given tools and implementation · Technical changes are absent · There is perfect contest · Product is measured in quantities. Increasing Returns to Scale Increasing returns to scale is closely associated with economies of calibration. Information technology occurs when a business firm increases its inputs, and a more-than-proportionate increase in production results For example, in yr one a house employs 200 workers, uses 50 machines, and produces one,000 products. In year two it employs 400 workers, uses 100 machines (inputs doubled), and produces ii,500 products (output more than doubled). Decreasing Returns to Scale Decreasing returns to scale is closely associated with diseconomies of scale. Decreasing returns to scale happens when the house'southward output rises proportionately less than its inputs ascension. For case, in year one, a business firm employs 200 workers, uses 50 machines, and produces ane,000 products. In year 2 it employs 400 workers, uses 100 machines (inputs doubled), and produces 1,500 products (output less than doubled). Constant Returns to Scale Abiding returns to scale occurs when the firm's output rises proportionate to the increase in inputs. Constant or same output. ii. Briefly explain about the types of cost concepts. — Types of toll concepts Actual costs and Opportunity Costs — Actual costs are too called every bit outlay costs, accented costs and conquering costs. — They are those costs that involve financial expenditures at some time and hence are recorded in the books of accounts. — o They are the actual expenses incurred for producing or acquiring a commodity or service by a business firm. — o For case, wages paid to workers, expenses on raw materials, power, fuel and other types of inputs. They can be exactly calculated and accounted without whatsoever difficulty. Opportunity toll of a good or service is measured in terms of acquirement which could have been earned past employing that good or service in some other culling uses. Direct costs are those costs which can be specifically attributed to a item production, a section, or a procedure of production. indirect costs are those costs, which are non traceable to any one unit of operation. They cannot be attributed to a product, a department or a process Explicit costs are those costs which are in the nature of contractual payments and are paid by an entrepreneur to the factors of product [excluding himself] in the form of hire, wages, interest and profits, utility expenses, and payments for raw materials etc. Implicit or imputed costs are implied toll.They do not take the form of greenbacks outlays and as such practise non appear in the books of accounts. They are the earnings of owner employed resources. Accounting costs are those costs which are already incurred on the product of a particular commodity.It includes just the acquisition costs. Economic costs are those costs that are to be incurred by an entrepreneur on various alternative programs. It involves the application of opportunity costs in conclusion makin ii). How to estimate the cost? Ø accounting concept Ø engineering concept Ø statistical toll iii. Explain well-nigh cost out put relation in brusk run &long run with not bad sketch. Ø Curt-run cost curves are normally based on a production function with one variable cistron of production that displays first increasing and then decreasing marginal productivity.Increasing marginal productivity is associated with the negatively sloped portion of the marginal toll curve, while decreasing marginal productivity is associated with the positively sloped portion. The average stock-still cost (AFC) curve is the cost of the fixed factor of production divided by the quantity of units of the output, while the average variable cost (AVC) curve cost traces out Ø the per unit price of variable factor of product.The U-shaped average total cost (ATC) curve is derived past adding the average fixed and variable costs. The marginal cost (MC) intersects both the AVC and ATC curves at their minimum points. Declining average full costs are explained as the effect of spreading the fixed costs over greater quantities and, at low quantities, the result of the increasing marginal productivity, in addition. Increasing average costs occur when the effect of failing marginal productivity overwhelms the effect of spreading the stock-still costs. LONG RUN: Ø The long-run price curves, commonly presented in a separate diagram, are also expressed most commonly in their boilerplate, or per unit of measurement, form, represented here in Figure 2. The long-run average Ø price (LRAC) bend is shown to be an envelope of the short-run boilerplate cost (SRAC) curves, lying everywhere below or tangent to the short-run curves. Ø The business firm is constrained in the shortrun in selecting the optimal mix of factors of production and so will never exist able to find a cheaper mix than tin be found in the long-run when there are no constraints. If at that place are a discrete number of institute sizes bachelor, the LRAC will be the scalloped bend obtained by joining those parts of the SRAC curves that represent the everyman cost of production for a given quantity. 4. Explain in detail about Total, Average & Marginal Costs. The cost concepts made utilise of in the toll behavior are Full cost, Average price, andMarginal toll. TC=TFC+TVC Ac=TC/Q Marginal Price is the improver to the total cost due to the production of an additional unit of measurement of production. -If both AFC and 'AVC' fall, 'ATC' will too autumn. Ø 'ATC' will fall where the drop in 'AFC' is more than the enhance in 'AVC'. Ø 'ATC' remains abiding is the drop in 'AFC' = ascent in 'AVC' Ø 'ATC' will rise where the drop in 'AFC' is less than the rise in 'AVC' Long Run Costs The long run is a planning and implementation stage for producers. They clarify the current and projected country of the market in order to make production decisions. Examples : irresolute the quantity of production, decreasing or expanding a company, and inbound or leaving a market. Interpretation of costs Accounting approaches It is classified as stock-still, variable and semi variable on the basis of judgment and inspection Fluctuation in output Maintenance of proper accounts Technology Approaches Information technology includes the physical units of diverse inputs every bit found size, materials etc., Statistical Approaches It includes Ø multiple correlations Ø Queuing theory Ø Input and output analysis 5. Calculate the Total, Boilerplate and Marginal Costs for the post-obit data. 
Study Fabric, Lecturing Notes, Assignment, Reference, Wiki description explanation, cursory particular
Engineering Economics and Financial Accounting : Production Function and Cost Anaysis : Important Questions and Answers: Production Function and Toll Analysis |
Source: https://www.brainkart.com/article/Important-Questions-and-Answers--Production-Function-and-Cost-Analysis_9259/
0 Response to "Chapter 13 the Costs of Production Questions for Review Answers"
Post a Comment